ALTERNATIVE TO POLYMER MESHES
BIOLOGICAL ENDOPROSTHESIS "HERNIOPLASTY"
Biological endoprosthesis "Hernioplasty"
Размеры
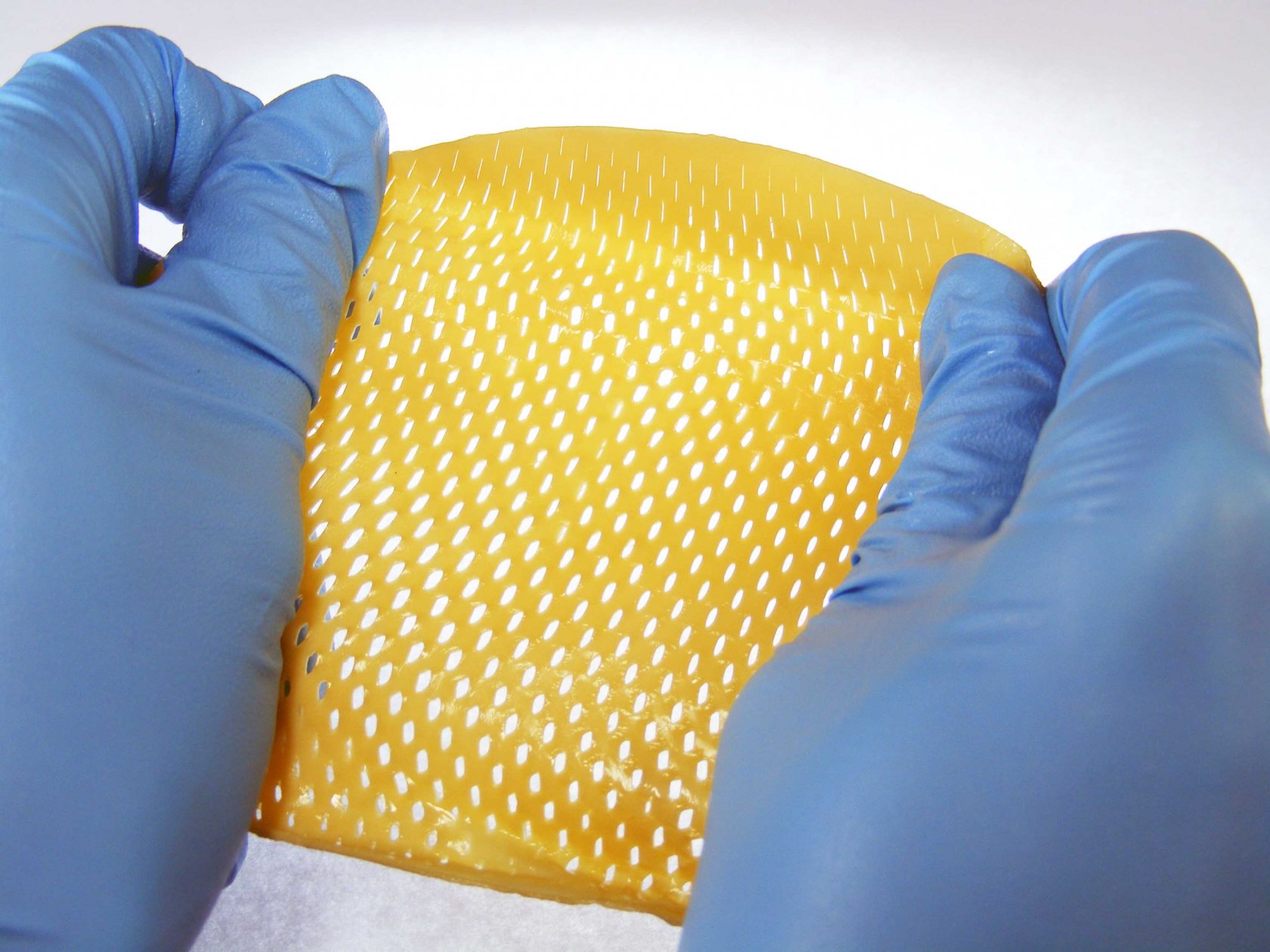
The implantable biological endoprosthesis for hernioplasty is made in the form of a mesh. The basis of the endoprosthesis is a nonimmunogenic biologically-compatible biological material of xenogenic origin. The biomaterial from which the endoprosthesis is made is a deep-purified decellularized collagen matrix, devoid of an antigen component. The endoprosthesis provides permanent strengthening of soft tissues and is an excellent alternative to synthetic meshes. Unlike synthetic analogues, it has a biological nature and it is completely absorbed and metabolized naturally, gradually being replaced by newly formed connective tissue. Does not form adhesions and scars. The endoprosthesis can have a round or rectangular shape. Individual pattern is available at the customer's request. Product thickness is from 0,3 to 1,3 mm. Plate perforation size - 2,5 mm with spacing of 2,5 mm. It is possible to manufacture any type of perforation at the customer's request. The maximum area of a rectangular endoprosthesis is 100 cm2; the maximum diameter of a round endoprosthesis is 130 mm.
The product is intended for permanent implantation in abdominal (for example, inguinal, postoperative ventral, umbilical, femoral) and other types of hernias.
The product is intended for permanent implantation in abdominal (for example, inguinal, postoperative ventral, umbilical, femoral) and other types of hernias.

Recurrent and repeatedly recurrent hernias
• Primary hernias of large size with a flabby abdominal wall due to muscle atrophy, fascia, aponeurosis
• Hernias with multiple herniated gates, when suturing the herniated gates does not give full confidence in their viability
• Placement of the prosthesis is possible using the methods of onlay, inlay, sublay
• Primary hernias of large size with a flabby abdominal wall due to muscle atrophy, fascia, aponeurosis
• Hernias with multiple herniated gates, when suturing the herniated gates does not give full confidence in their viability
• Placement of the prosthesis is possible using the methods of onlay, inlay, sublay
- compared with synthetic analogues, it has a biological nature and is involved in metabolism according to natural laws, gradually being replaced by newly formed connective tissue
- it has a high rate of biological integration
- it resists the infectious process and mechanical impact
- it is well modeled on the operating field
- it provides reliable strengthening of the abdominal wall defect
- is resistant to eruption by surgical threads
- it ensures that the transplant does not erupt the patient's nearby organs and tissues
- it carries risks of minimal prosthetic-associated purulent-inflammatory complications
- it is not encapsulated and does not leave a feeling of a foreign body in the postoperative period
- minimizes the formation of serous fluid collections, fistulas, shriveling of the prosthesis, the formation of coarse fibrous connective tissue in the zone of hernioplasty, the severity of pain
- the biological endoprosthesis for hernioplasty must be fixed to the edges of the aponeurosis by a continuous suture with absorbable monofilament threads 2/0-3/0. It can be fixed with biological glue
- in cases where the aponeurosis defect exceeds the maximum size of the endoprosthesis, it is possible to use two or more flaps sewn together by a continuous seam with absorbable monofilament threads 2/0-3/0
- after carrying out xenoplasty in all cases, vacuum redon drainage should be performed directly on the operating table, immediately after completion of surgical intervention
The endoprosthesis can have a round or rectangular shape. Individual pattern is available at the customer's request. Product thickness is from 0,3 to 1,3 mm. Plate perforation size - 2,5 mm with spacing of 2,5 mm. It is possible to manufacture any type of perforation at the customer's request. The maximum area of a rectangular endoprosthesis is 100 cm2; the maximum diameter of a round endoprosthesis is 130 mm.

The product is in a sterile double package with instructions for use. Additionally, the product can be equipped with a sterile container for low vacuum drainage.
The product is supplied in a proprietary preservative solution. The duration of washing in a sterile normal saline solution is 4 minutes.
The product is supplied in a proprietary preservative solution. The duration of washing in a sterile normal saline solution is 4 minutes.
- Connective tissue synthesis activity one year after the implantation of the biological endoprosthesis is 28% higher than that obtained in the tissues around the polypropylene mesh.
- Prosthetic hernioplasty of mid-ventral hernias with a biological endoprosthesis preserves the physiological mobility of the abdominal rectus muscles. Due to bioresorption, the endoprosthesis does not prevent repeated operations after earlier hernioplasty.
- Hernioplasty using a biologic endoprosthesis reduces the duration of pain by an average of 0,47 days, reduces the absolute risk of postoperative complications by 5,58%, and reduces the patient's hospital stay by an average of 3,89 bed days (p<0,05)
- Using the method of hernioplasty with a biological endoprosthesis significantly improved the quality of life of patients in the long term after surgery, reducing the number of patients experiencing pain and foreign body sensation at the site of surgery by an average of 44,34% compared to patients who used polypropylene mesh as a hernioprosthesis. *
- The method of laparostomy formation using a biological endoprosthesis for hernioplasty allows avoiding such complications as eventration, traumatization of intestinal loops, and the formation of intestinal fistulas.
